The Ultimate Guide to Warehouse Racking Systems [2024]
The Ultimate Guide to Warehouse Racking Systems for Space Optimization
Table of Contents
Introduction to Warehouse Racking Systems
In the quest for efficient warehouse management, understanding and selecting appropriate warehouse racking systems or storage equipment is vital. Warehouse racking systems are used for holding or buffering materials over a period of time. But, storage solutions are not just about storing materials and product; they’re about optimizing space and product flow, enhancing accessibility, and ensuring material safety. Let’s examine the different warehouse racking systems utilized in a warehouse and provide practical tips for efficient space management.
Types of Storage Equipment
Block Stacking
Block Stacking. Block stacking is a storage method that involves stacking unit loads, such as boxes, pallets, or products, one on top of another on the warehouse floor without the use of racks. Depending on the type of product being handled, the goods may or may not be palletized.
For pallet floor storage, these are typically arranged in lanes. The depth of a lane is determined by the number of pallets placed back-to-back, and the height is measured by the maximum number of pallets stacked on top of each other. The entire footprint of a lane is reserved for a single SKU if any part of it is storing a pallet. Each column is also assigned a single SKU for ease of tracking.
Block stacking can be beneficial in warehouses with abundant floor space and low SKU diversity. One of the main advantages of block stacking is that it doesn’t require any racking, which makes it the most cost-effective solution. However, it can limit accessibility to stored items. This method optimizes warehouse space by removing unnecessary aisles and stacking loads to increase volume, as opposed to placing only one pallet on the floor. Below we list some of the pros and cons of block stacking.
Pros and Cons of Block Stacking
- Economical: Block stacking is the most economical as it does not require any racking.
- Maximized Space: space is optimized by eliminating aisles and by stacking loads (versus storing only one pallet on the floor.)
- SKU Control: It is essential to group a single SKU in high-density clusters to efficiently stack blocks, controlling the stock and easily locating each product.
However, there are significant disadvantages with block stacking that need to be taken into account. These include:
- Height limitations: This depends on the type of load stored. If a large amount of product is stacked, the structure could become unstable and collapse. Racks, on the other hand, can guarantee storage of loads at great heights.
- Damage to goods: If the weight of the stacked load is too heavy, the merchandise located on the lower levels could become damaged.
- Risk of accidents: Racks are sturdy and remain intact, minimizing impacts from handling equipment and ensuring total stability of the loads they hold. Block stacking doesn't have these benefits, making it more prone to risks and accidents.
Selective Pallet Rack
Selective Pallet Rack offers easy access to each pallet. They are the most popular type of storage rack and are ideal for warehouses with a wide variety of products. Each pallet in the rack is independently accessible thanks to load-supporting beams. This means that any SKU can be retrieved from any pallet location, regardless of the level of the rack. While this provides complete freedom to retrieve any individual pallet, it does require relatively more aisle space to access the pallets since an aisle is required for each row of selective rack. Roll-Formed Teardrop rack is the industry standard for punching styles on selective pallet racking. The term “teardrop” comes from the shape of the connection slots that are built into the pallet rack uprights. Selective rack is typically configured in either Single-Deep rack or Double-Deep rack. Single-deep racks allow direct access to each pallet while Double-Deep racks increase storage density.
Single-Deep Rack
This type of rack allows for fast and complete 100% accessibility to all loads with no honeycomb loss. However, single-deep selective rack may result in low cube utilization due to aisle space requirements – selective rack requires an aisle for every row of rack.
Double-Deep Rack
Double-Deep rack essentially consists of two single-deep racks placed one in front of the other so pallets are stored two deep. Due to the load-supporting beams, each 2-deep lane is independently accessible, and so any SKU can be stored in any lane at any level of the rack. To avoid double-handling each lane is filled with a single SKU.
Double-Deep rack is a Last In First Out (LIFO) system. Since this type of rack stores two pallets per position, it provides greater cube utilization than single-deep racks. Double-Deep rack can increase pallet storage by as much as 20-40% depending on racking layout.
However, reaching the rear load in the rack requires an extended reaching mechanism on the lift truck. This type of racking also reduces the amount of accessible SKUs due to 50% of SKUs being behind pallets when storage locations are at full capacity. Double-deep racks are typically used when the inventory level for an item is at least five or when loads are stored and picked in multiples of two pallets. Bottom line: If you have multiple pallets of the same SKU, will benefit from higher density storage, and are able to sacrifice some selectivity, then Double-Deep rack may be right for you.
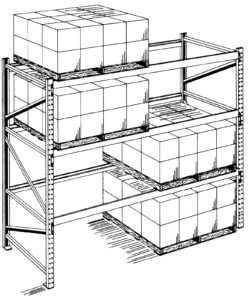
Push-Back Pallet Rack
Push-Back rack is a gravity flow racking system that allow pallets to be stored 2 to 6 pallets deep on either side of an aisle. This is easy to visualize as an extension of Double-deep rack but extended up to 6 pallet positions, but to make the interior pallet positions accessible, the rack in each lane pulls out like a drawer. This means that each lane (at any level) is independently accessible. Push-Back Rack is ideal for storing multiple pallets of the same SKU per lane. They are a high-density storage solution that provides efficient use of space and provides LIFO storage in each lane where pallets are loaded and unloaded at the lower end and closed at the higher end.
There are generally two types of Push-Back Rack, a Push-Back Flow System and the more traditional Push-Back Cart System:
Push-Back Rack Flow System
A Push-Back Pallet Flow System is a storage system that consists of a wheeled or roller lane that is installed on a slight slope. The system is designed to be loaded and unloaded from a single aisle. The single-aisle access reduces the racking system’s overall footprint and can be placed up against a wall since the loading and unloading aisle are on the same side.
To load the system, the forklift operator places the first pallet in the lane, and then pushes it back as subsequent pallets are loaded. As the pallets are removed, the remaining pallets flow forward automatically due to the slope of the lane. This system is designed to optimize storage space as it allows multiple pallets to be stored in a single lane.
The forklift operator has control over the speed of the flow by backing out of the system at a safe speed. The system is designed to automatically replenish the pick face with the next pallet as pallets are removed from the lane. This ensures that the pick face is always stocked and that the system is optimized for efficiency.
Push-Back Flow Systems require good condition pallets to flow properly. In a flow lane, if there are broken or missing boards, or nails protruding, can cause the pallet to get hung up in the lane or even damage the flow rails.
One advantage of this type of Push-Back rack system is in addition to storing standard GMA pallets, these systems can be used with non-standard pallets and a range of sizes. (In fact, we’ve designed this type of system around specialty motorcycle skids that measure 43″ x 104″.) Another advantage of a Push-back flow system is the ability to create deep lane storage of up to 12 pallets deep.
Push-Back Rack Cart System
Push-Back Rack Cart Systems are the more traditional system that store pallets on wheeled carts nesting on inclined storage rails. This racking system features nested carts, which sit at the front of the beams. When a pallet is loaded, an existing pallet and cart will be pushed back with the newly-loaded pallet resting on the cart that was nested below the first. A Push-Back Cart System is best suited for standard GMA-style pallets. Advantages: 1) Pushback carts and rails are generally cheaper. 2) Performance can be better with pallets that aren’t all high quality. Pallet quality is not as crucial as it is in flow rack applications. 3) Structural steel pushback carts are more abuse resistant versus flow rack components. One disadvantage of this traditional design is limited lane depths. The complexity of the cart/track interface combined with cart stacking heights, limits the depth of traditional push-back rack to a maximum of 6 pallets deep – with the most commonly used systems being 2-3 deep. For higher-density lanes, a push-back flow system is recommended with its ability to accommodate much deeper lanes.
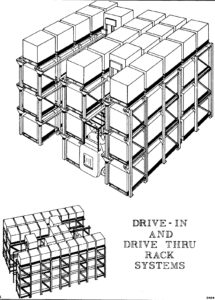
Drive-In and Drive-Through Racks
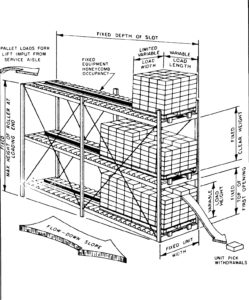
Drive-In Rack and Drive-Through Rack are storage systems that enable lift trucks to access the interior loads of a rack frame. However, these systems require that all the levels of each lane are solely dedicated to a single Stock Keeping Unit (SKU) to avoid double-handling. In Drive-In Rack, the retrieval and put-away functions are executed from the same aisle, whereas, in Drive-Through Rack, pallets enter from one end of the lane and exit from the other in a First-In-First-Out (FIFO) manner. Drive-In/Through Rack serves as floor-storage for non-stackable products, but it is not as flexible as other types of pallet rack systems. Additionally, it has some limitations. For instance, each pallet is supported only by the edges, necessitating strong pallets. Furthermore, it necessitates a highly skilled forklift driver to navigate within the lane, which can be costly. Storage and retrieval times with Drive-In are longer due to the care required by the forklift driver while inside the Drive-in system.
Drive-in pallet rack presents an effective storage solution for warehouses that store a large quantity of pallets with similar products. While standard selective pallet rack meets the needs of many warehouses, those with a substantial volume of like-products with a substantial amount of pallets stand to benefit from the use of drive-in pallet rack. This type of racking system allows for high-density storage, which is crucial for businesses that require efficient use of floor space. By utilizing the drive-in pallet rack system, businesses can ensure that their products are organized, secure, and easily accessible.
Pallet Flow Rack/Flow-Through Rack
Pallet Flow Racks, also referred to as Flow-Through Rack, represent a storage system for pallets that relies on the forces of gravity and wheels or rollers to facilitate the flow and accumulation of pallets within a lane. The depth of pallet flow racks may vary from two to more than twenty pallets deep, resulting in a higher storage density than that of other forms of racking. Powered by gravity, the self-transportation of pallets from the load end to the unload end necessitates a reduced amount of forklift travel, and different forklift operators can independently load and unload pallets.
The Flow-Through concept is that pallets are loaded from the back of the system. When a pallet is removed from the front, the pallets behind it roll–or flow–forward automatically towards the unloading position (FIFO system). The pallets roll on flow rails at a pitch determined by the weight of the skids. Speed controllers are installed in the flow-through lanes to ensure safe travel of the pallet to the unloading end.
When determining the optimal wheel for a pallet flow rack system, multiple factors must be taken into account. Foremost among these is the pallet depth and application. If the system is to be utilized solely for picking operations and is two to three pallets deep, steel skatewheels with a diameter of 1.9″ may be deemed appropriate. For deeper gravity flow rack storage lanes, larger diameter and wider polycarbonate wheels are generally recommended. For heavy pallet loads over 3,000 lbs., there are 2.9″ diameter reinforced resin wheels that are rated up to 330 lbs each. Alternatively, rollers are often utilized in cases where the bottom of the pallet is not conducive to the use of wheels.
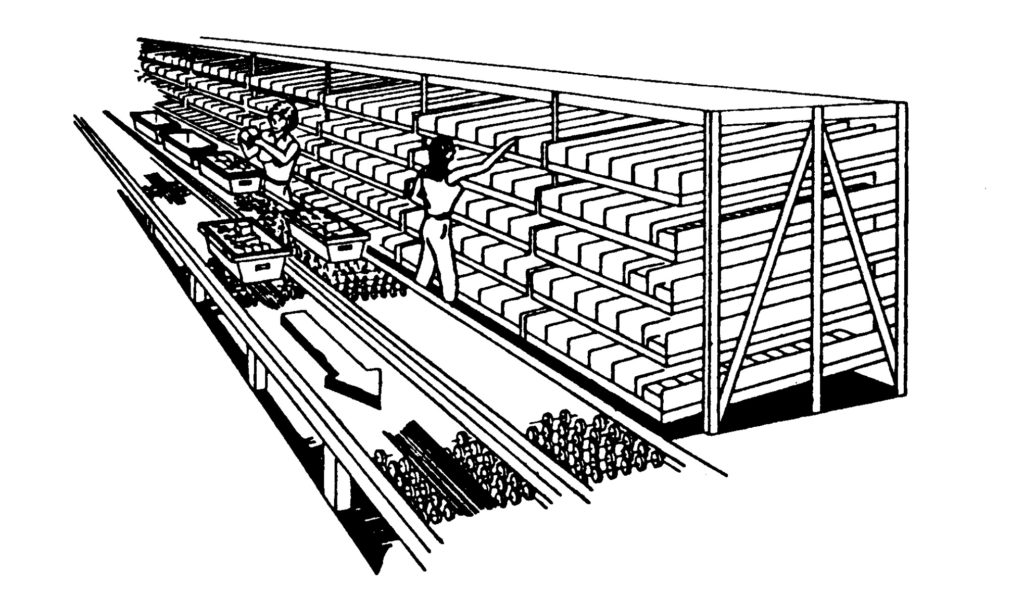
Carton Flow Rack
Carton Flow Rack is the same concept as Pallet Flow, but on a different scale. Carton Flow Rack is mainly used in distribution warehouses for fast fast-moving items. Flow lanes are customized to individual SKUs. A Carton Flow System can help increase product deployment speed and efficiency. This type of system can help improve your pick rates and reduce labor costs.
Carton Flow rack is a special type of shelving with shelves that are tilted with rollers to bring cartons or cases forward for picking. The shelves may be 3–10 feet deep. This means that only one case of a product needs to be on the pick-face, which means that many SKUs can be available in a small area. This means higher SKU-density which tends to increase the pick-density, decrease travel, and increase picks/person-hour.
The picking from carton flow rack is often enhanced by supporting technology such as pick-to-light systems, by which a centralized computer lights up lights or LEDs on racks or shelves at every location within a bay from which product is to be picked. After the worker picks the appropriate quantity, who pushes a button to signal the computer. There are several benefits of this: The order-picker is freed from handling a paper pick-list they do not have to search for the next storage location, and because picking is guided, it is more accurate. A typical pick rate from carton flow rack is about 150–500 picks/person-hour, but this varies widely. When carton flow is combined with a pick-to-light system pick rates of as high as 800 picks per hour have been seen.
Carton Flow rack is restocked from the back and this is done independently of picking. This means that restocking never interferes with picking (as is the case for static shelving) for which picking and restocking need to alternate. However, additional aisle space is required to access the back of carton flow rack for restocking.
There are several subtypes of Carton Flow Rack that assist in different types of picking applications:
- Standard rack design with vertical frame: This is the most common type of carton flow rack which has a flush/square pick face. These square front systems are best suited to picking full cases (see photo on left).
- Layback frame: slants back slightly to present the front pick position of each level more fully to the order picker. Best suited for picking from open cases from cartons in varying size. The slant is customizable, but approximately 10 degrees is fairly common. Occupies more space than the standard flush design (see middle photo).
- Front-tilted shelves: As a carton approaches the pick face, it is directed onto a front-tilted shelf or tilt tray because of the angled flow lane and the advancing rear cartons. This makes it easier to identify the carton for picking and places it in a more comfortable and ergonomic position. Best suited for picking from open cases when cases are similar in size (see photo on right).
Cantilever Rack
If you have ever walked into your local Home Depot store into the lumber section, you have seen the Cantilever racking that store their long-length products and lumber products. Cantilever racks are uniquely designed for long, odd-shaped, bulky items, and other long raw material handling supplies such as lumber, plywood, wood, or pipes. Their open-front structure allows easy access to stored items and can be tailored for both lightweight and heavyweight materials.
With Cantilever rack, the loads are supported by two or more cantilevered “arms” (the arms are horizontal beams supported at only one end) Cantilever racks are available in two designs: single-sided and double-sided. The single-sided cantilever rack is installed against a wall in a warehouse and provides storage on one side only. On the other hand, the double-sided cantilever rack can be accessed from both sides, offering more storage capacity. However, it requires more floor space compared to the single-sided cantilever rack.
They are similar to pallet racking, except the front upright and front shelf beams are eliminated.
Cantilever rack is used when there is a need for a full clear shelf that can be loaded from the front without obstruction from the uprights.
Shelving Systems
Shelving systems offer a versatile and cost-effective solution for storing small, loose, non-palletized items. These systems range from simple bin shelving, where items are placed directly on shelves or in bins/cartons.
Advantages: Low cost; economical
Disadvantages: Can result in excessive travel for pickers. May be difficult to pick from top shelf depending on the height of the picker and the weight of the product. Replenishment can interfere with picking.
Several levels of shelves (and storage drawers) on a mezzanine can be used to allow multi-level picking (max 4 levels) this is typically referred to as a Shelving Mezzanine. A lift truck or VRC (vertical reciprocating conveyor) can be used to help with removing product from the top level.
There are various types of shelving systems some of the most common types of shelving systems we have listed below.
Industrial Steel Shelving
If you’re looking for traditional, metal-style shelving with a flat metal shelf, this is your choice. Industrial Steel Shelving can be adaptable to virtually any storage situation to meet light-duty storage needs to the heaviest duty. This shelving can be configured to handle loads between 350 lbs. to 1,350 lbs. Shelves sit on clips making them easily adjustable. Industrial Steel Shelving is ideal for various applications in the garage, office, or industrial warehouse storage. An Open Shelving unit has X-bracing at the sides and back which provides rigidity for storing oversized or larger items. Open Unit Shelving is the foundation of any well-planned and general-purpose storage solution. Open Shelving is dependable and has the flexibility to be used in virtually any application where accessibility is important.
A Closed shelving unit has rigid metal panels at the sides and back. Closed Shelving has an aesthetically pleasing appearance along with excellent structural integrity. The applications for closed shelving units are endless: from stock room shelving to retail storage, or for the office – Closed Shelving systems are the perfect storage solution for applications that require more protection compared to open units. Accessories for our shelving systems include shelf dividers, label holders, and footplates.
Whether you need open or closed shelving ultimately depends on your industrial storage needs. Industrial steel shelving has many applications – generally speaking, if you are looking for greater accessibility, easy visibility of items, and more economical shelving, consider choosing open-style shelving. If a more finished look, durability, and protective storage is more of a priority, consider closed-style shelving.
Rivet Style Boltless Shelving
Rivet Style Boltless Shelving has evolved into a versatile storage solution, widely adopted across various industries. Initially predominant in bulk and archive storage, its usage now spans retail, healthcare, garage, office, filing, and warehouse storage – accommodating needs of all scales.
Key Features of Rivet Style Boltless Shelving
- Efficient Assembly: Boltless design allows for quick assembly with just a mallet, cutting installation costs by 30-40%.
- Durability: Composed of robust 14 gauge and 16 gauge steel components, ensuring structural integrity.
- Accessibility: Designed with open-style units, providing four-sided access to stored items.
- Beam Variety: Four beam types available to meet a wide range of storage needs, accommodating shelf sizes from 12” x 12” to 48” x 96”.
- Decking Options: Includes Particle Board, Melamine Coated Particleboard (MCP), and Wire Decking, offering flexibility in shelving surfaces.
Typical Applications of Rivet Style Boltless Shelving
- Office and Filing Storage: Efficiently organizes office supplies, archives, and filing materials.
- Retail Storage: Ideal for storing shoes, apparel, electronics, boxed merchandise, cosmetics, appliances, and RTA furniture.
- Material Handling Storage: Suitable for parts, warehouse equipment, and tools.
- Healthcare Storage: Useful for archival records, linens, and medical supplies.
- Restaurant Storage: Accommodates food, beverages, supplies, and equipment.
L&T Shelving
L&T Shelving, also known as Four-Post Shelving, is the number one alternative to conventional drawer file storage. Ideal for law firms and archive storage applications looking for a more luxurious feel to their space. Vertical file storage increases storage capacity by up to 60% compared with conventional filing equipment, but also makes files more accessible. The available custom wood fascia gives this shelving an ultra premium look that we’ve installed in many prestigious law offices, libraries, and office spaces to date. L&T Shelving offers the unique ability to expand as your needs change – at any time WITHOUT the need for tools. There are a wide variety of optional features and accessories such as: optional shelf supports that attach to mobile carriages, a reference shelf, dividers, and more. Easy assembly in minutes without any tools!
Wire Shelving
Wire Shelving offers a reliable and code-compliant solution for diverse environments, including food service, clean rooms, and medical facilities.
Key Features of Wire Shelving
- Durability: Crafted from 12-gauge steel, capable of supporting loads up to 1,000 lbs.
- Size Range: Available in a variety of widths, from 24” to 72″, accommodating various space requirements.
- Design Efficiency: The open design of the shelving minimizes dust accumulation, ensuring a cleaner environment.
- Ease of Assembly: Tool-free construction allows for straightforward setup and modification.
- Versatility: Suitable for both freestanding and mobile applications.
Advanced Storage Solutions
We will add several more systems to this section in the coming weeks including Carousels, Vertical Lift Modules, A-Frames, Automated Storage and Retrieval systems (AS/RS) and more – stay tuned!
Mobile Racking
Sliding Racks, more commonly referred to as Mobile Racking Systems or Mobile Racks, are dynamic storage solutions designed to maximize warehouse space efficiency. These systems consist of conventional shelving units mounted on powered movable carriages that slide laterally along rails embedded in the floor. Mobile racks provide high-cube utilization.
How Do Mobile Racks Work?
The key feature of a mobile rack system is its mobility. At the touch of a button or the turn of a mechanical-assist handle, entire shelving units can be compacted together or moved apart to create an aisle where access is needed. This movement is facilitated by electronically powered bases known as “carriages” that glide smoothly on tracks/rails, allowing for quick and effortless reconfiguration of the storage space.
Advantages of Mobile Racks
- Space Optimization: By eliminating the need for multiple fixed aisles, mobile racks can double or even triple storage capacity within the same footprint, making them ideal for warehouses where space is at a premium.
- Accessibility: Despite their high-density design, these systems provide complete accessibility to all stored goods, as any rack can be moved to retrieve items without disturbing others.
- Customization: Sliding racks can be tailored to fit various warehouse layouts and can accommodate a range of shelving options and storage unit sizes.
- Enhanced Security: These systems often come with integrated safety features and can be locked down to secure inventory, which is particularly advantageous in regulated environments.
Disadvantages of Sliding Racks
- Cost: The initial investment for mobile racking systems is higher than for static storage solutions due to their mechanical and electronic components.
- Retrieval Time: While access to goods is direct, it can be time-consuming if the desired item is located deep within a compacted row, as the system requires the opening and closing of aisles.
- Power Dependence: The electric-powered systems rely on a reliable power source for operation, which can be a limitation in areas prone to power outages or where electrical infrastructure is not robust.
- Maintenance: The mechanical and electronic components of sliding racks require regular maintenance to ensure smooth operation.
Ideal Applications for Mobile Racks
Mobile rack systems are typically found in environments where high-density storage is necessary, and space utilization is a priority. They are well-suited for:
- Library Stacks: For archiving books, manuscripts, and media.
- Vaults: Secure storage for valuable items or sensitive documents.
- Climate-Controlled Storage Rooms: Such as refrigerated warehouses for food and beverage or pharmaceuticals.
Choosing the Right Storage System for Your Warehouse
Selecting the right pallet rack system for your business can be daunting due to significant capital expenditure and numerous variables in design and function. It’s crucial to conduct thorough research and seek expert advice to make an informed decision aligned with your business objectives, storage requirements, and budget. To help you find the best storage solution for your unique needs, let’s start by setting you on the right track. Refer to the table below for an at-a-glance comparison of different storage solutions to determine what best fits your space and budget. This table helps simplify some complex data and provides some rules of thumb. The cost per pallet position below is intended solely for ROM (rough order of magnitude) or high-level budgetary estimates for easy cost comparison. Keep in mind that prices consistently fluctuate with the price of steel, supply and demand, and many other factors.
To get an approximation for installation costs, installation costs typically range between 15% and 40% of the equipment cost depending on the type of warehouse racking system and several other factors. Selective pallet rack installation costs may range between 15% to 25% of equipment costs where a high-density dynamic storage system like Push-back racking or Pallet Flow racking may range between 25% to 35% of equipment costs. For the most accurate pricing, please consult with a material handling systems expert at Storage Coordinators.
| Type of Racking | Cost per pallet position (est.) | Storage depth per lane | Inventory level per SKU | All loads accessible | Storage/Retrieval throughput | FIFO retrieval possible | Vertical honeycomb loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Block Stacking | – | 2-10 | > 5 | No | Good | Yes | Yes |
| Single Deep | $75 – $200 | 1 | < 3 | Yes | Good | Yes | No |
| Double Deep | $80 – $200 | 2 | > 5 | No | Average | No | No |
| Drive In | $200 – $400 | 5-10 | ≥ 20 | No | Average | No | Yes |
| Drive Through | $200 – $400 | 5-10 | ≥ 20 | No | Average | Yes | Yes |
| Push Back | $250 – $500 | 2-12* | 3-10 | No | Good | No | No |
| Pallet Flow | $375 – $500 | 2-20 | 3-10 | No | Excellent | Yes | No |
| Mobile Racks | – | 1 | < 3 | Yes | Poor | Yes | No |
Optimizing your warehouse space with the right storage systems and equipment is crucial for operational efficiency. Storage Coordinators is here to guide you in selecting the most suitable storage solutions for your needs. Contact us today to enhance your warehouse’s functionality and productivity or to request a storage consultation.
Contact Us
FILL OUT THE FORM BELOW AND OUR STORAGE EXPERTS WILL GET BACK TO YOU WITHIN 1 BUSINESS DAY.
Warehouse Rack Consultation
Storage Coordinators stands out as a preeminent authority in the field of material handling systems integration and consulting. Our expertise is unparalleled in the industry, and we work diligently to provide best-in-class solutions to our clients. Our expert team brings a wealth of experience to the task of integrating various storage systems for our clients. Whether it be racking, shelving, automation, or other types of storage solutions, we have the knowledge and skills necessary to create a comprehensive and efficient storage solution that meets your specific needs. Our team is committed to providing high-quality service and working closely with our clients to ensure that their storage needs are fully met. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you optimize your storage operations.
Benefits of Storage Consultation
- Increase Productivity
- Reduce Labor Costs
- Increase Storage Capacity
- Unbiased Storage Rack and Forklift Opinions
- Racking Style Determination
- Project Management